Sensitivity of lysozyme crystallization to temperature variation†
Abstract
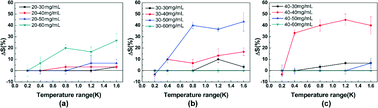
Environments with varying temperatures have been shown to beneficially increase the probability of obtaining protein crystals. Therefore, a cycling temperature strategy (CTS) has been proposed for protein crystallization screening. During the practical application of this strategy, it is necessary to know the effective temperature range that promotes crystallization to design a suitable temperature program. In this paper, the effects of different temperature ranges on lysozyme crystallization (or more specifically, nucleation) were investigated. The results show that a small periodic variation in the temperature range of as little as 0.4 K can have a significant effect on the crystallization success rate under some crystallization concentration conditions, confirming that crystallization of lysozyme is very sensitive to temperature variation. Because practical protein crystallization is always performed in an environment with slight temperature variations, the sensitivity of protein crystallization to temperature may provide an explanation for the poor reproducibility of protein crystallization. Further investigation of the CTS on lysozyme crystallization showed that a cycling temperature strategy exerts an effect on protein crystallization by altering the supersaturation caused by changes in temperature.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...