Heparin triggered dose dependent multi-color emission switching in water: a convenient protocol for heparinase I estimation in real-life biological fluids†
Abstract
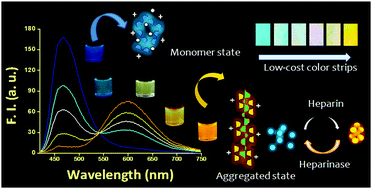
Oligo(p-phenylenevinylene) based bis-pyridinium derivatives show ‘ratiometric’ detection of heparin in water. For the first time, we present a dose-dependent, multi-color emission switching in the presence of heparin. The reversible self-assembly of probes with heparin as the stimulus is also exploited for the screening of heparinase I enzyme.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...