Guanidiniocarbonyl pyrrole (GCP) conjugated PAMAM-G2, a highly efficient vector for gene delivery: the importance of DNA condensation†
Abstract
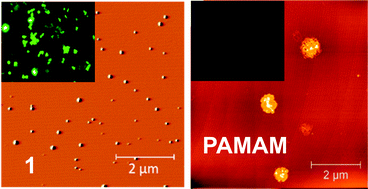
A novel hybrid compound 1 efficiently shuttles genetic material into HeLa cells at concentrations as low as 0.6 μM, whereas the parent compound PAMAM-G2 is ineffective even at 200 μM. The high efficiency of 1 stems from its capabiliy to form highly condensed ligand–DNA polyplexes. Its binding affinity is actually lower than for the parent dendrimer. Compound 1 is even 200 times more effective and less cytotoxic than PEI, the current gold standard in gene transfection with cationic polymers.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...