Discrete polygonal supramolecular architectures of isocytosine-based Pt(ii) complexes at the solution/graphite interface†
Abstract
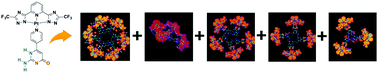
Polygonal supramolecular architectures of a Pt(II) complex including trimers, tetramers, pentamers and hexamers were self-assembled via hydrogen bonding between isocytosine moieties; their structure at the solid/liquid interface was unravelled by in situ scanning tunneling microscopy imaging. Density functional theory calculations provided in-depth insight into the thermodynamics of their formation by exploring the different energy contributions attributed to the molecular self-assembly and adsorption processes.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...