Regulating the antibiotic drug release from β-tricalcium phosphate ceramics by atmospheric plasma surface engineering
Abstract
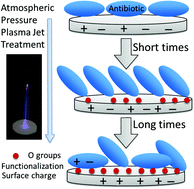
Calcium phosphate (CaP) ceramics are of interest in bone substitution due to their good biocompatibility and bioresorbability. Currently certain CaPs in the market are loaded with antibiotics in order to prevent infections but further control is needed over antibiotic release patterns. Cold plasmas have emerged as a useful means of modifying the interactions with drugs through surface modification of polymer materials. In this work we explore the possibility of using atmospheric pressure plasmas as a tool for the surface modification of these CaP materials with newly populated bonds and charges, with views on enabling higher loading and controlled drug release. Herein the surface modification of β-tricalcium phosphate ceramics is investigated using an atmospheric pressure helium plasma jet as a tool for tuning the controlled release of the antibiotic doxycycline hyclate, employed as a drug model. The surface chemistry is tailored mainly by plasma jet surface interaction with an increasing O/C ratio without changes in the topography as well as by build-up of surface charges. With this surface tailoring it is demonstrated that the atmospheric plasma jet is a new promising tool that leads to the design of a control for drug release from bioceramic matrices.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...