Signal-on electrochemical sensor for the detection of two analytes based on the conformational changes of DNA probes†
Abstract
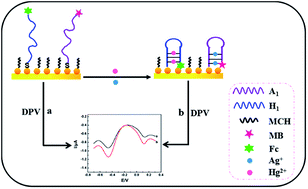
In this study, we reported a sensing strategy for the simultaneous determination of two analytes based on the conformational change of DNA probes. Mercury ions (Hg2+) and silver ions (Ag+) were selected as target analytes. The strategy involved specific DNA probes (containing rich thymine (T) or cytosine (C) bases) labeled with ferrocene (Fc) or methylene blue (MB), and gold nanoparticles (Au NPs) immobilized on the electrode surface. In the presence of target analytes, because of the specific interaction of T and C bases with Hg2+ and Ag+, respectively, the formation of T–Hg2+–T and C–Ag+–C complexes induced large conformational changes of the DNA probes from open structures to “hair-like” structures, which made the signal molecules of Fc and MB closer to the electrode surface. The resulting changes clearly improved the electrochemical signal intensity. Under optimal conditions, the signal intensity changes were linearly related to the concentration of the two analytes in the range 0.1–30 nM for Hg2+ and 0.1–40 nM for Ag+, and the limit of detection for the two analytes was as low as 0.05 nM (S/N = 3). When the sensor was applied to the analysis of real water samples, satisfactory results were obtained.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...