Fluorescence turn-on for the highly selective detection of nitric oxide in vitro and in living cells†
Abstract
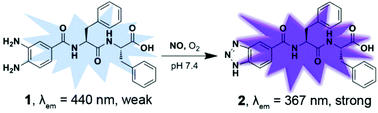
Nitric oxide (NO) is the first ubiquitous signaling molecule in the human body. The selective and sensitive detection of NO in vitro and in vivo is of high importance but remains challenging. Previous fluorescent probes for NO detection either are of poor water solubility or lack selectivity over intracellular biomolecules. Herein, we rationally designed a water-soluble, biocompatible, small molecular probe o-phenylenediamine-Phe-Phe-OH (1) for the highly selective and sensitive detection of NO in vitro and in living cells. 1 can react with NO and turn on the fluorescence emission at 367 nm via an ICT mechanism. In vitro tests indicated that 1 showed high selectivity for NO detection without interference from common anions, ROS/RNS, and intracellular biomolecules DHA, AA, or MGO. In PBS buffer, 1 was applied for detecting NO within the range of 0–12 μM with a LOD of 6 nM. Moreover, 1 was successfully applied to sense intracellularly generated NO in living cells. We anticipate that 1 could be potentially employed for studying the toxicity and bioactivity of NO in the near future.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...