A lipopolysaccharide binding heteromultivalent dendrimer nanoplatform for Gram negative cell targeting†
Abstract
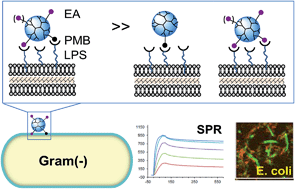
We report on the practicality of a heteromultivalent design strategy for a nanoplatform that targets lipopolysaccharide molecules (LPS) present on the surface of Gram-negative bacteria. This design is based on the conjugation of a poly(amido amine) (PAMAM) dendrimer with two types of ligands, each having distinct affinities: (i) polymyxin B (PMB) as a primary high affinity ligand; (ii) a PMB-mimicking dendritic branch as an auxiliary low affinity ligand. Co-conjugation of these two ligands maximizes the efficiency of the primary ligand even when the primary ligand is present at a low valency on the nanoplatform (mean nPMB ≈ 1). By performing surface plasmon resonance studies using a LPS-immobilized cell wall model, we identified an ethanolamine (EA)-terminated branch as the auxiliary ligand that promotes binding avidity via heteromultivalent association. PMB conjugation of the dendrimer with excess EA branches led to LPS avidity two orders of magnitude greater than unconjugated PMB. Such tight binding observed by SPR corresponded well with adsorption to E. coli cells and with potent bactericidal activity in vitro.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...