Ultrasound coating of polydimethylsiloxanes with antimicrobial enzymes
Abstract
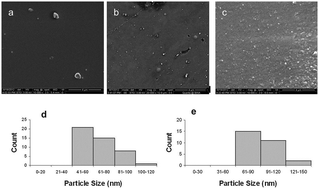
There is an urgent need for antimicrobial functionalization of urinary catheters to prevent microbial colonization and biofilm formation on them. Here, the antimicrobial hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) producing enzyme cellobiose dehydrogenase (CDH) was for the first time grafted onto polydimethylsiloxanes (PDMS) using an ultrasound assisted coating method. This resulted in the development of an effective in situ continous H2O2 producing system able to continuously prevent microbial colonization and biofilm formation on catheters. This enzyme has an added advantage that it uses various oligosaccharides including expolysaccharides (an important part of the bioflim produced by the microbes while colonizing biomaterials) as electron donors to produce H2O2. Successful immobilization of active CDH nanoparticles on PDMS was confirmed by ESEM and AFM analysis as well as quantification of H2O2. Depending on the initial enzyme concentration, CDH-nanoparticles of varying sizes from 65 ± 17 nm to 93 ± 17 nm were created by the ultrasonic waves and subsequently deposited on the PDMS surface. PDMS sheets treated for 3 min produced 18 μM of H2O2 within 2 hours which was sufficient to significantly reduce the amount of viable S. aureus cells as well as the total amount of biomass deposited on the surface. The ultrasound assisted coating of antimicrobial enzymes therefore provides an easy approach to immobilize enzymes and create a surface with antimicrobial properties.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...