Core cross-linked nanogels based on the self-assembly of double hydrophilic poly(2-oxazoline) block copolymers†
Abstract
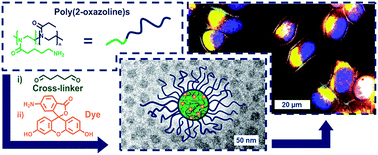
The synthesis of poly(2-oxazoline)-based block copolymers consisting of a cationic and a hydrophilic segment is described. The self-assembly of these macromolecules in organic solvents results in the formation of micelles and vesicles, respectively, depending on the solvent used. To transfer the systems into water, cross-linking using glutaraldehyde was applied, followed by the consumption of excessive aldehyde functions by either diethylamine or 6-aminofluorescein (6AF). The cross-linked assemblies were analyzed regarding their size and shape by electron microscopy and light scattering methods, as well as for their chemical composition by solid state NMR spectroscopy. 6AF associated samples were examined with respect to their absorption and fluorescence behavior in aqueous environment, revealing an alkaline microenvironment within the presented nanostructures. The toxicity of the systems against mouse fibroblast cell line L929 was examined by the XTT assay and was found to be insignificant for concentrations of up to 2.5 mg mL−1. Flow cytometry and fluorescence microscopy analysis revealed an efficient concentration and time dependent cellular uptake of the nanogels.
- This article is part of the themed collection: 2015 Journal of Materials Chemistry B Hot Papers

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...