Hygrothermal simulation-informed design of mesoporous desiccants for optimised energy efficiency of mixed mode air conditioning systems
Abstract
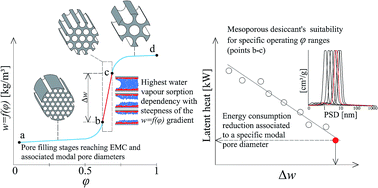
This paper describes an optimization technique using hygrothermal numerical modelling to determine an ideal and unknown isotherm in order to inform the design of optimised mesoporous desiccants. Their suitability for passive humidity buffering as well as their impact on energy efficiency was assessed when assisting a mixed mode air-conditioning (AC) system. Three clear stages of water vapour adsorption were found that strongly correspond to the Δw gradient when assessing the kinetics of adsorption and exchange rates for periodic moisture loads. Consistent agreement was found between the latent heat of dehumidification used by the AC system and the desiccant decay time after successive sorption loop cycles. This confirmed the material's suitability for specific applications and was found to be highly sensitive to the portion of the isotherm between φi,L − φi,U (Δw gradient), compared with full adsorption capacity (total w) when assessing total energy consumption. The experimental results of sorption kinetics appeared to be slightly underestimated between the Δw gradient and the response time to reach equilibrium moisture content (EMC). The major underestimations were found to be consistent with the kinetics of adsorption/desorption when analysing their significance based on w differences. These were largely attributed to a combination of adsorption kinetics (time-response) and adsorption/desorption hysteresis. However, this was not evident when comparing long-term experimental data and numerical estimations for water vapour sorption isotherms, since numerical model accurately predicted them. This suggests that both adsorption kinetics and the scanning curve prediction, within a hysteresis loop, are not accurately represented by current hygrothermal models and are hence a priority for future research.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...