Cycling performance of lithium-ion polymer cells assembled with a cross-linked composite polymer electrolyte using a fibrous polyacrylonitrile membrane and vinyl-functionalized SiO2 nanoparticles
Abstract
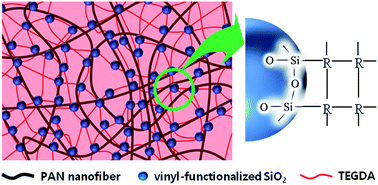
Vinyl-functionalized SiO2 nanoparticles were synthesized and uniformly dispersed on the surface of a fibrous polyacrylonitrile (PAN) membrane for use as cross-linking sites. A composite polymer electrolyte was prepared by in situ cross-linking between vinyl-functionalized SiO2 particles on the PAN membrane and the electrolyte precursor containing tri(ethylene glycol) diacrylate. The cross-linked composite polymer electrolyte effectively encapsulated the electrolyte solution without leakage. It exhibited good thermal stability as well as favorable interfacial characteristics toward electrodes. Lithium-ion polymer cells composed of a graphite negative electrode and a LiNi0.8Co0.15Al0.05O2 positive electrode were assembled with the in situ cross-linked composite polymer electrolyte. The cells with cross-linked composite polymer electrolytes using the fibrous PAN membrane and vinyl-functionalized SiO2 particles exhibited high discharge capacity and good capacity retention at both ambient temperature and elevated temperature.
- This article is part of the themed collection: 2015 Journal of Materials Chemistry A Hot Papers

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...