Functionalized graphene/Fe3O4 supported AuPt alloy as a magnetic, stable and recyclable catalyst for a catalytic reduction reaction†
Abstract
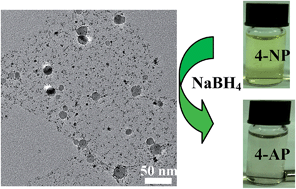
Herein, branched poly-(ethylenimine) functionalized graphene/iron oxide hybrid (termed as BGNs/Fe3O4) was chosen as an efficient support material to load AuPt alloy nanoparticles for constructing a multifunctional nanocatalyst via a simple and controlled self-assembly approach. BGNs/Fe3O4 as a nanocarrier made the AuPt alloy nanoparticles uniformly distributed on the surface of BGNs/Fe3O4. The obtained multifunctional nanocatalyst was characterized by high-resolution transmission electron microscopy (HRTEM), energy dispersive X-ray (EDX) spectroscopy, UV-Vis spectroscopy and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS). The nanocatalyst exhibited favorable water solubility, excellent dispersion, good stability, superparamagnetism and particularly high catalytic activity for reducing 4-nitrophenol (4-NP). Furthermore, by tuning the composition of the nanoalloy nanoparticles of the multifunctional nanocatalyst, a normalized rate constant of about 17.99 mg−1 s−1 was achieved, which was superior to most of the Au or Pt based nanocatalysts reported in recent years. In addition, it was proved that the magnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles not only ensured the reuse of the nanocatalyst, but also significantly improved the catalytic activity. Thanks to the favorable catalytic activity, the obtained multifunctional nanocatalyst may hold great potential for various catalytic processes.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...