Investigation of pH-induced conformational change and hydration of poly(methacrylic acid) by analytical ultracentrifugation†
Abstract
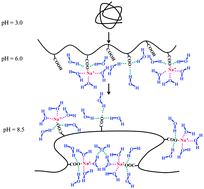
Analytical ultracentrifugation was performed on poly(methacrylic acid) (PMAA) with a series of weight average molar masses (Mw) in aqueous solutions as a function of pH. The scales of the sedimentation coefficient (s) and the diffusion coefficient (D) to Mw at infinite dilutions were obtained at different pH values, indicating that PMAA chains adopt a collapsed structure at low pH values, and stretch at pH higher than 5.2. Our results show that the sedimentation coefficient exhibits a minimum at pH ∼ 6.0, presumably due to the effect of the conformational change and the hydration state of PMAA chains. When pH increases from 6.0 to 8.5, PMAA chains with high molar mass shrink a little bit, presumably because the sodium ions act as a bridging agent between nonadjacent carboxylate groups. Furthermore, the weight average molar mass of PMAA at pH 8.5 increases by one fold than that at pH 4.0, indicating the condensation of sodium ions and the increase in the number of hydration water molecules around carboxylate groups at high pH values.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...