Molecular architecture requirements for polymer-grafted lignin superplasticizers†
Abstract
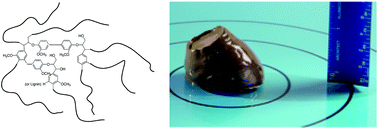
Superplasticizers are a class of anionic polymer dispersants used to inhibit aggregation in hydraulic cement, lowering the yield stress of cement pastes to improve workability and reduce water requirements. The plant-derived biopolymer lignin is commonly used as a low-cost/low-performance plasticizer, but attempts to improve its effects on cement rheology through copolymerization with synthetic monomers have not led to significant improvements. Here we demonstrate that kraft lignin can form the basis for high-performance superplasticizers in hydraulic cement, but the molecular architecture must be based on a lignin core with a synthetic-polymer corona that can be produced via controlled radical polymerization. Using slump tests of ordinary Portland cement pastes, we show that polyacrylamide-grafted lignin prepared via reversible addition-fragmentation chain transfer polymerization can reduce the yield stress of cement paste to similar levels as a leading commercial polycarboxylate ether superplasticizer at concentrations ten-fold lower, although the lignin material produced via controlled radical polymerization does not appear to reduce the dynamic viscosity of cement paste as effectively as the polycarboxylate superplasticizer, despite having a similar affinity for the individual mineral components of ordinary Portland cement. In contrast, polyacrylamide copolymerized with a methacrylated kraft lignin via conventional free radical polymerization having a similar overall composition did not reduce the yield stress or the viscosity of cement pastes. While further work is required to elucidate the mechanism of this effect, these results indicate that controlling the architecture of polymer-grafted lignin can significantly enhance its performance as a superplasticizer for cement.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...