The icephobic performance of alkyl-grafted aluminum surfaces†
Abstract
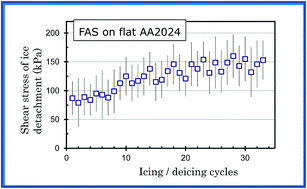
This work analyzes the anti-icing performance of flat aluminum surfaces coated with widely used alkyl-group based layers of octadecyltrimethoxysilane, fluorinated alkylsilane and stearic acid as they are subjected to repeated icing/deicing cycles. The wetting properties of the samples upon long-term immersion in water are also evaluated. The results demonstrate that smooth aluminum surfaces grafted with alkyl groups are prone to gradual degradation of their hydrophobic and icephobic properties, which is caused by interactions and reactions with both ice and liquid water. This implies that alkyl-group based monolayers on aluminum surfaces are not likely to be durable icephobic coatings unless their durability in contact with ice and/or water is significantly improved.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...