Formation and characterization of a reactive chromium(v)–oxo complex: mechanistic insight into hydrogen-atom transfer reactions†
Abstract
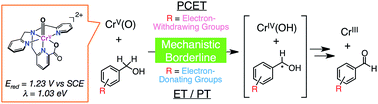
A mononuclear Cr(V)–oxo complex, [CrV(O)(6-COO−-tpa)](BF4)2 (1; 6-COO−-tpa = N,N-bis(2-pyridylmethyl)-N-(6-carboxylato-2-pyridylmethyl)amine) was prepared through the reaction of a Cr(III) precursor complex with iodosylbenzene as an oxidant. Characterization of 1 was achieved using ESI-MS spectrometry, electron paramagnetic resonance, UV-vis, and resonance Raman spectroscopies. The reduction potential (Ered) of 1 was determined to be 1.23 V vs. SCE in acetonitrile based on analysis of the electron-transfer (ET) equilibrium between 1 and a one-electron donor, [RuII(bpy)3]2+ (bpy = 2,2′-bipyridine). The reorganization energy (λ) of 1 was also determined to be 1.03 eV in ET reactions from phenol derivatives to 1 on the basis of the Marcus theory of ET. The smaller λ value in comparison with that of an Fe(IV)–oxo complex (2.37 eV) is caused by the small structural change during ET due to the dπ character of the electron-accepting LUMO of 1. When benzyl alcohol derivatives (R-BA) with different oxidation potentials were employed as substrates, corresponding aldehydes were obtained as the 2e−-oxidized products in moderate yields as determined from 1H NMR and GC-MS measurements. One-step UV-vis spectral changes were observed in the course of the oxidation reactions of BA derivatives by 1 and a kinetic isotope effect (KIE) was observed in the oxidation reactions for deuterated BA derivatives at the benzylic position as substrates. These results indicate that the rate-limiting step is a concerted proton-coupled electron transfer (PCET) from substrate to 1. In sharp contrast, in the oxidation of trimethoxy-BA (Eox = 1.22 V) by 1, trimethoxy-BA radical cation was observed by UV-vis spectroscopy. Thus, it was revealed that the mechanism of the oxidation reaction changed from one-step PCET to stepwise ET–proton transfer (ET/PT), depending on the redox potentials of R-BA.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...