Cytocompatible in situ cross-linking of degradable LbL films based on thiol–exchange reaction†
Abstract
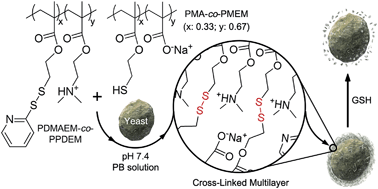
Formation of both mechanically durable and programmably degradable layer-by-layer (LbL) films in a biocompatible fashion has potential applications in cell therapy, tissue engineering, and drug-delivery systems, where the films are interfaced with living cells. In this work, we developed a simple but versatile method for generating in situ cross-linked and responsively degradable LbL films, based on the thiol–exchange reaction, under highly cytocompatible conditions (aqueous solution at pH 7.4 and room temperature). The cytocompatibility of the processes was confirmed by coating individual yeast cells with the cross-linked LbL films and breaking the films on demand, while maintaining the cell viability. In addition, the processes were applied to the controlled release of an anticancer drug in the HeLa cells.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...