The chemical stability and cytotoxicity of carbonyl iron particles grafted with poly(glycidyl methacrylate) and the magnetorheological activity of their suspensions†
Abstract
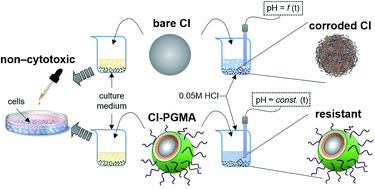
Carbonyl iron (CI) particles were grafted with poly(glycidyl methacrylate) (PGMA) using atom transfer radical polymerization. Compact coating of PGMA largely improved the chemical stability of the particles in an acid environment and thus reduced the common drawback of bare CI particles. Furthermore, due to possible medical applications of CI-polymer systems for magnetic drug targeting, an in vitro cytotoxicity test was performed using an NIH/3T3 cell line. The cell viability was evaluated by spectrometric assay (MTT). The results show that the prepared particles are not cytotoxic. Moreover, bare CI particles as well as synthesized core–shell particles were suspended in silicone oil, and the rheological behavior of MR suspensions was investigated in controlled shear rate mode under various magnetic field strengths. Dynamic yield stress as a measure of the rigidity of the created internal structures of the suspensions was determined using the Herschel–Bulkley model, which provided a reasonably good fit for rheological data. MR suspensions of PGMA-coated particles exhibited only slightly decreased yield stresses due to their negligibly-affected magnetic performance.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...