Synthesis, optical properties, and photochemical activity of zinc-indium-sulfide nanoplates†
Abstract
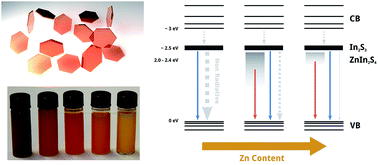
Zinc indium sulfide is an interesting material for photocatalytical applications. Here, ZnxIn2S3+x nanoplates with varying value of x (between 0 and 1) were synthesized by means of colloidal chemistry. The nanoplates have a diameter of up to 100 nm and a relatively small thickness of 2.5 nm. The structure of the Zn-free particles could be assigned to β-In2S3 based on the powder X-ray diffraction and Raman spectroscopy data. Particles containing Zn exhibit the hexagonal ZnIn2S4 structure. The samples were studied by steady state and time resolved photoluminescence spectroscopy. Our results demonstrate that increasing amounts of Zn incorporation result in more intra-gap states that participate in radiative sub-band gap recombination and simultaneously decrease non-radiative defect states that might, for example, originate from vacancies in the structure. Furthermore, the nanoplates exhibit significantly increased photochemical activity in the degradation of rhodamine 6G, depending on their Zn content. The high surface-to-volume ratio and the intra-gap states might be responsible for this finding.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...