In situ monitoring of palladacycle-mediated carbonylation by surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy†
Abstract
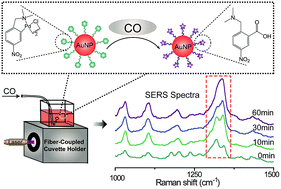
Palladium-catalyzed carbonylation has emerged as one of the most potential approaches for the synthesis of carbonyl-containing molecules, however, the understanding remains challenging in many reactions partly because of a lack of robust monitoring methods. Herein, we report a novel surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) based strategy for the in situ monitoring of palladacycle-mediated carbonylation. The nanoplatforms integrated with SERS activity and reaction mediability were constructed through assembling new synthesized palladacycles (PCs) on the surface of gold nanoparticles. It was shown that, when carbon monoxide (CO) was introduced to the nanoplatform-containing system as a C1 source, palladacycle-mediated carbonylation was initiated, and the SERS spectra of the nanoplatforms changed concomitantly. With this SERS spectrum variation, the reaction mechanism could be investigated facilely, and the corresponding reaction was found to follow a pseudo-first-order kinetics rate law based on the relationship between the relative ratiometric peak intensities of I1319/I1338 and the reaction time. Therefore, using the proposed SERS approach, the carbonylation process could be directly monitored in situ without tedious pretreatments.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...