Ceria nanoparticles with rhodamine B as a powerful theranostic agent against intracellular oxidative stress†
Abstract
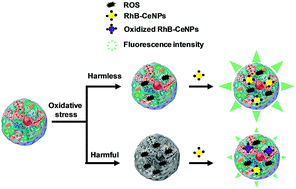
Ceria nanoparticles with rhodamine B groups covalently attached on their surface (RhB-CeNPs) were successfully prepared to simultaneously exhibit antioxidant activity and the ability to detect oxidant species. In order to use them for biomedical purposes, the nanoparticles were internalized in two human cell lines (HeLa and Hep3B), confirmed by confocal microscopy. In addition, their biocompatibility was assessed by performing proliferation, viability and apoptosis assays, in which they showed a remarkable lack of toxicity. Thereafter, the antioxidant activity of RhB-CeNPs against reactive oxygen species (ROS) in a model of oxidative stress was demonstrated in HeLa cells using the dichloro-dihydro-fluorescein diacetate (DCFH-DA) assay. RhB-CeNPs exhibited higher cytosolic antioxidant activity than the well-established ceria nanoparticles. Surprisingly, the antioxidant capacity of RhB-CeNPs was evident when the ROS content of the cells increased notably (and was, therefore, harmful for those cells). Furthermore, the ability of RhB-CeNPs as ROS-content sensors was evaluated by measuring oxidative stress in HeLa cells using the intrinsic fluorescence of the rhodamine B groups present on the nanoparticles. The results with respect to the detection and quantification of ROS were similar to those obtained with DCFH-DA, a typical method of quantifying intracellular ROS. Our results demonstrate the potential of RhB-CeNPs as remarkably biocompatible theranostic agents with application in the field of oxidative stress.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...