Gallic acid and methyl-3-O-methyl gallate: a comparative study on their effects on prostate cancer stem cells
Abstract
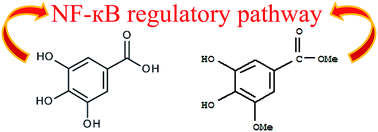
Growing evidence shows that gallic acid (3,4,5-trihydroxybenzoic acid, GA) and methyl-3-O-methyl gallate (M3OMG) possess physiological and pharmacological activities as antioxidant and anti-inflammatory agents. At the molecular level, many chronic diseases, including cancer, are caused by oxidative stress and deregulated inflammatory responses. Several lines of evidence support a role for oxidative stress and inflammation in cancer. Moreover, one of the most important links between inflammation and cancer is nuclear factor κB (NF-κB), a transcription factor regulating the expression of genes involved in inflammation and immune responses. The aim of the present study is twofold: to evaluate and compare the ability of GA and M3OMG to inhibit NF-κB transcriptional activity, and to address their properties in different prostate cancer cell subpopulations. NF-κB transcriptional activity was found to be higher in prostatosphere than in prostate cancer cells cultured as an adherent monolayer and was efficiently reduced by GA and M3OMG. M3OMG exhibited stronger inhibitory activity in cancer cells with stem-like properties, whereas GA exhibited higher potency in the more differentiated cancer cells and was more effective in blocking cellular proliferation. Moreover, M3MOG was a stronger inhibitor of prostatosphere formation than GA. These results show that GA and M3OMG inhibit NF-κB transcriptional activity and growth of prostate cancer cells, with differential effects on cells with different proliferative, self-renewal and tumourigenic potential.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...