Geopolymerization with bagasse bottom ash and china clay, effect of calcination temperature and silica to alumina ratio
Abstract
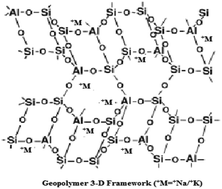
The object of this work to study geopolymerization using bagasse ash and china clay at the most appropriate calcination temperature and ratio of silica to alumina. Bagasse ash from the sugar industry and china clay from Shah Dheri Swat in Pakistan were used in this work. Both of the raw materials were characterized using XRF, FTIR and XRD. The clay was calcined between a temperature range of 600–1000 °C. The resulting amorphous material was reacted with bagasse ash and sodium silicate using different ratios of silica to alumina ranging from 2–4. The reaction was carried out in a strongly alkaline solution of sodium hydroxide to produce geopolymer cement whose compressive strength and setting time were studied. The geopolymer cement specimens were characterized using XRF, XRD and SEM. The highest compressive strength for the geopolymers of 16.64 MPa was obtained from the mix having a SiO2/Al2O3 ratio of 2.7 and clay calcined at a temperature of 900 °C.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...