Facile synthesis of monodisperse poly(MAA/EGDMA)/Fe3O4 hydrogel microspheres with hollow structures for drug delivery systems: the hollow structure formation mechanism and effects of various metal ions on structural changes†
Abstract
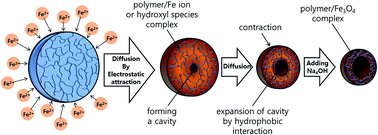
This study presents a facile fabrication method for monodisperse poly(methacrylic acid/ethylene glycol dimethacrylate)/Fe3O4 [poly(MAA/EGDMA)/Fe3O4] composite microcapsules with magnetic properties and hollow structures for use as a targeted drug delivery system. In aqueous solution, the iron ions diffuse into the negatively-charged spherical polymer particles by electrostatic attraction. Since the obtained polymer–metal complexes decrease the repulsive force between the negatively-charged carboxyl groups of the polymer chains, the chelating parts of the polymer particles lose their hydrophilic properties and become relatively hydrophobic. As the number of iron ions continues to increase in the polymer particles, an internal cavity begins to be formed by interaction between the hydrophobic domains and the inner polymer chains. After the reducing agent is added into the synthetic system, Fe3O4 nanoparticles formed in the shells of the polymer particles retain the hollow structure. Confocal laser scanning microscopy and zeta potential measurements are employed to confirm the formation of the hollow structure during the diffusion of the various metal ions into the polymer gel. The magnetic properties of the poly(MAA/EGDMA)/Fe3O4 composite microcapsules synthesized under diverse experimental conditions are characterized by a vibrating sample magnetometer. The controlled release behavior of the model drug doxorubicin hydrochloride from the polymer–metal hollow composite microcapsules is investigated under different pH conditions.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...