Gold nucleation inhibition by halide ions: a basis for a seed-mediated approach†
Abstract
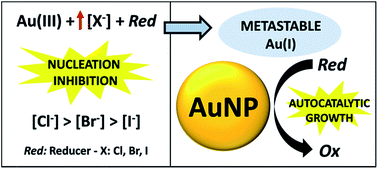
In the present work, we examine the effect of halide ions on gold nucleation, a typical synthetic variable in the wet-chemical production of gold nanostructures. It was found that the homogeneous nucleation of gold by the chemical reduction of aqueous gold ions is kinetically quenched by an increase in the concentration of halide ions, and this effect grows stronger as the Au–halide complex stability increases. The nucleation quenching is not exclusively related to a specific reducing agent, but appears to be a more general behavior, and is affected by the pH of the media. While no nucleation is observed, Au(I) metastable species coexist together with the reducer, constituting metastable solutions. It is demonstrated that nucleation inhibition by halide ions can be employed as a basis for a seed-mediated approach to produce gold nanostructures. The metastable solutions are proved to function as growth baths, where Au(I) reduction is triggered on the surface of previously synthesized gold nanoparticles, driving their growth in the absence of secondary nucleation. It is also shown how, with this approach, the synthesis conditions can be rationally designed to obtain gold nanoparticles with the desired properties in a controlled and reproducible fashion.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...