Thermoresponsive self-assembled NiPAm-zwitterion copolymers†
Abstract
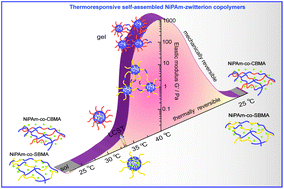
Zwitterionic polymers are well known for their non-fouling properties due to their unique pendant side chain structures. In this work, we incorporated temperature-responsive N-isopropylacrylamide (NiPAm) with zwitterionic monomers (carboxybetaine methacrylate (CBMA) and sulfobetaine methacrylate (SBMA)), and synthesized the statistical copolymers poly(NiPAm-co-CBMA) and poly(NiPAm-co-SBMA). Above the low critical solution temperature (LCST), a clear sol–gel transition was observed, accompanied by an increase in the turbidity and elastic modulus of the copolymer solution. The self assembly and thermoresponsive properties of these statistical copolymers under large strains and different temperatures were characterized by UV-visible spectroscopy, dynamic light scattering, and rheological characterizations. We showed that poly(NiPAm-co-CBMA) copolymers consisted of both mechanically and thermally reversible networks, favoring them as reusable and biocompatible elastic materials. As a comparison, incorporating SBMA with NiPAm inhibited the thermo-sensitive and viscoelastic features of the pure NiPAm based polymer, causing a delayed LCST and a weakened viscoelastic response in poly(NiPAm-co-SBMA) copolymers at both room and body temperatures. Our work demonstrates that CBMA monomers in a poly(NiPAm-co-CBMA) copolymer act as stronger ionic bridges to form elastic networks when compared with a poly(NiPAm-co-SBMA) copolymer. As a result, poly(NiPAm-co-CBMA) possesses both non-fouling and thermo-sensitive features, without compromised mechanical properties.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...