Synthesis of multifunctional poly(1-pyrenemethyl methacrylate)-b-poly(N-isopropylacrylamide)-b-poly(N-methylolacrylamide)s and their electrospun nanofibers for metal ion sensory applications†
Abstract
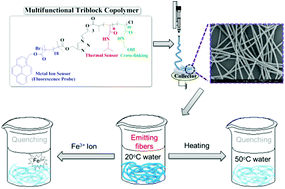
We report the synthesis and characterization of multifunctional triblock copolymers, poly(1-pyrenemethylmethacrylate)-block-poly(N-isopropylacrylamide)-block-poly(N-methylolacrylamide) (PPy-b-PNIPAAm-b-PNMA), and their electrospun (ES) nanofibers for temperature or metal-ion sensing. The triblock copolymers are composed of fluorescent and metal-ion-sensitive PPy, thermoresponsive PNIPAAm, and chemically crosslinkable PNMA segments. Non-crosslinked ES nanofibers are initially prepared using the aforementioned PPy-b-PNIPAAm-b-PNMA triblock copolymers followed by thermal crosslinking. It is found that ES nanofibers prepared from PPy-b-PNIPAAm-b-PNMA can self-assemble to form nano-scale spherical aggregates with PNMA located at the core, PNIPAAm at the center layer, and PPy at the shell. This self-assembly characteristic therefore induces a strong excimer emission between the pyrenyl moieties. The crosslinking process between PNMA blocks is then implemented to stabilize the ES nanofibers since the non-crosslinked ones are metastable objects. The resulting crosslinked nanofibers exhibit a predominant wettability and dimension stability under aqueous states, and can perform a detectable photoluminescence transition at different temperatures or toward an Fe3+ ion. In contrast to their counterpart drop-cast film, ES nanofibers with a high surface/volume ratio have obviously higher sensing ability toward thermal stimuli and metal ions, and are expected to be applied as multifunctional sensory devices.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...