The low photo-inactivation rate of bacteria in human plasma II. Inhibition of methylene blue bleaching in plasma and effective bacterial destruction by the addition of dilute acetic acid to human plasma
Abstract
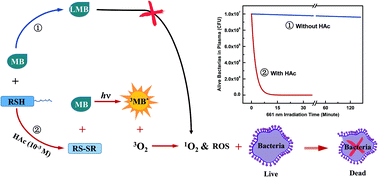
Methylene blue (MB) and other photo-sensitizer molecules have been recognized as effective means for the inactivation of bacteria and other pathogens owing to their ability to photo-generate reactive oxygen species (ROS) including singlet oxygen. These reactive species react with the membrane of the bacteria causing their destruction. However, the efficiency of MB to destroy bacteria in plasma is very low because the MB 660 nm absorption band, that is responsible for the ROS generation, is bleached. The bleaching of MB, in plasma, is caused by the attachment of a hydrogen atom to the central ring nitrogen of MB, which destroys the ring conjugation and forms Leuco-MB which does not absorb in the 600 nm region. In this paper we show that addition of dilute acetic acid, ∼10−4 M, to human plasma, prevents H-atom attachment to MB, allowing MB to absorb at 660 nm, generates singlet oxygen and thus inactivates bacteria. The mechanism proposed, for preventing MB bleaching in plasma, is based on the oxidation of cysteine to cystine, by reaction with added dilute acetic acid, thus eliminating the availability of the thiol hydrogen atom which attaches to the MB nitrogen. It is expected that the addition of acetic acid to plasma will be effective in the sterilization of plasma and killing of bacteria in wounds and burns.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...