Spray deposited β-Bi2O3 nanostructured films with visible photocatalytic activity for solar water treatment†
Abstract
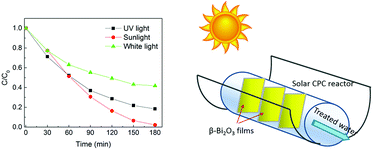
Bismuth oxide thin films were obtained by the spray pyrolysis method using bismuth acetate as the precursor salt. The films were characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR), UV-vis diffuse reflectance, X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS) and Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM). The XRD patterns indicated that the pure β phase is obtained at 450 °C and was also confirmed by FTIR. This phase presents a nanoplate morphology which is adequate for the photocatalytic reactions. Moreover, the band gap value was 2.6 eV indicating a good capacity of visible light absorption. The photocatalytic degradation of the Methyl Orange (MO) dye was pH dependent, an acid solution being easier to degrade. However, the Bi2O3 films were easily converted into BiOCl when they were in contact with a solution containing HCl. In order to preserve the β-Bi2O3 phase, the Acid Blue 113 dye with its natural pH of 8 was used to evaluate the stability of the photocatalytic activity after five degradation cycles. The photoactivity was practically stable indicating a good performance of the material. This encouraged us to test the films in a continuous flow solar reactor prototype for the degradation of the dye solution using sunlight radiation exclusively. The good performance of the β-Bi2O3 films indicates that they can be used for sustainable water treatment applications.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...