Cationic dialkylarylphosphates: a new family of bio-inspired cationic lipids for gene delivery†
Abstract
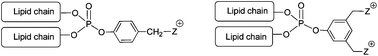
In this work that aims to synthesize and evaluate new cationic lipids as vectors for gene delivery, we report the synthesis of a series of cationic lipids in which a phosphate functional group acts as a linker to assemble on a molecular scale, two lipid chains and one cationic polar head. The mono or dicationic moiety is connected to the phosphate group by an aryl spacer. In this work, two synthesis strategies were evaluated. The first used the Atherton–Todd coupling reaction to introduce a phenolic derivative to dioleylphosphite. The second strategy used a sequential addition of lipid alcohol and a phenolic derivative on POCl3. The two methods are efficient, but the latter allows larger yields. Different polar head groups were introduced, thus producing amphiphilic compounds possessing either one permanent (N-methyl-imidazolium, pyridinium, trimethylammonium) or two permanent cationic charges. All these cationic lipids were formulated as liposomal solutions and characterized (size and zeta potential). They formed stable liposomal solutions both in water (at pH 7.0) and in a weakly acidic medium (at pH 5.5). Finally, this new generation of cationic lipids was used to deliver DNA into various human-derived epithelial cells cultured in vitro. Compared with Lipofectamine used as a reference commercial lipofection reagent, some cationic dialkylarylphosphates were able to demonstrate potent gene transfer abilities, and noteworthily, monocationic derivatives were much more efficient than dicationic analogues.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...