Enzymatically degradable hybrid organic–inorganic bridged silsesquioxane nanoparticles for in vitro imaging†
Abstract
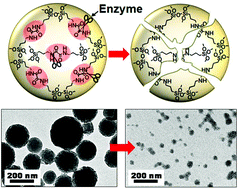
We describe biodegradable bridged silsesquioxane (BS) composite nanomaterials with an unusually high organic content (ca. 50%) based on oxamide components mimicking amino acid biocleavable groups. Unlike most bulk BS materials, the design of sub-200 nm nearly monodisperse nanoparticles (NPs) was achieved. These enzymatically degradable BS NPs were further tested as promising imaging nanoprobes.
 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...