An ultrastable conjugate of silver nanoparticles and protein formed through weak interactions†
Abstract
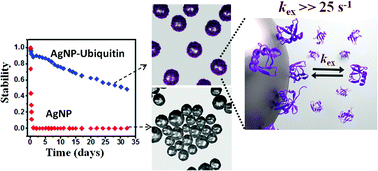
In recent years, silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) have attracted significant attention owing to their unique physicochemical, optical, conductive and antimicrobial properties. One of the properties of AgNPs which is crucial for all applications is their stability. In the present study we unravel a mechanism through which silver nanoparticles are rendered ultrastable in an aqueous solution in complex with the protein ubiquitin (Ubq). This involves a dynamic and reversible association and dissociation of ubiquitin from the surface of AgNP. The exchange occurs at a rate much greater than 25 s−1 implying a residence time of <40 ms for the protein. The AgNP–Ubq complex remains stable for months due to steric stabilization over a wide pH range compared to unconjugated AgNPs. NMR studies reveal that the protein molecules bind reversibly to AgNP with an approximate dissociation constant of 55 μM and undergo fast exchange. At pH > 4 the positively charged surface of the protein comes in contact with the citrate capped AgNP surface. Further, NMR relaxation-based experiments suggest that in addition to the dynamic exchange, a conformational rearrangement of the protein takes place upon binding to AgNP. The ultrastability of the AgNP–Ubq complex was found to be useful for its anti-microbial activity, which allowed the recycling of this complex multiple times without the loss of stability. Altogether, the study provides new insights into the mechanism of protein–silver nanoparticle interactions and opens up new avenues for its application in a wide range of systems.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...