Ultrasensitive SERS detection of trinitrotoluene through capillarity-constructed reversible hot spots based on ZnO–Ag nanorod hybrids†
Abstract
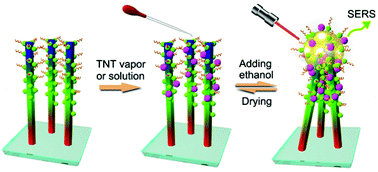
A simple and efficient self-approach strategy was used to apply ultrasensitivity and self-revive ZnO–Ag hybrid surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) sensors for the highly sensitive and selective detection of explosive TNT in both solution and vapour conditions. The good ultrasensitive sensing performance is a result of the abundant Raman hot spots, which were spontaneously formed in a reversible way by the self-approaching of flexible ZnO–Ag hybrid nanorods driven by the capillary force of solvent evaporation. Moreover, the enhancement effect was repeatedly renewed by the reconstruction of molecular bridges, which could selectively detect TNT with a lower limit of 4 × 10−14 M. In addition, TNT vapor was also tested under this sensor, whereby once the ZnO–Ag NRs hybrid substrate was dipped in TNT, this substrate could detect the existence of TNT even in 5 detection cycles via a capillarity-constructed reversible hot spots approach. Compared with other pure Ag-based SERS sensors, this ZnO–Ag hybrid SERS sensor could rapidly self-revive SERS-activity by simple UV light irradiation and could retain stable SERS sensitivity for one month when used for TNT detection. This stable and ultrasensitive SERS substrate demonstrates a new route to eliminate the oxidized inactive problem of traditional Ag-based SERS substrates and suggests promising use in the applications of such hybrids as real-time online sensors for explosives detection.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...