Broadband infrared photoluminescence in silicon nanowires with high density stacking faults†
Abstract
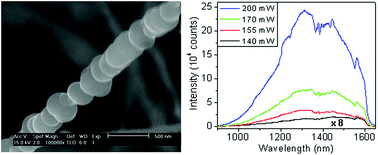
Making silicon an efficient light-emitting material is an important goal of silicon photonics. Here we report the observation of broadband sub-bandgap photoluminescence in silicon nanowires with a high density of stacking faults. The photoluminescence becomes stronger and exhibits a blue shift under higher laser powers. The super-linear dependence on excitation intensity indicates a strong competition between radiative and defect-related non-radiative channels, and the spectral blue shift is ascribed to the band filling effect in the heterostructures of wurtzite silicon and cubic silicon created by stacking faults.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...