Synthetic strategies to achieve further-functionalised monoaryl phosphate primary building units: crystal structures and solid-state aggregation behavior†
Abstract
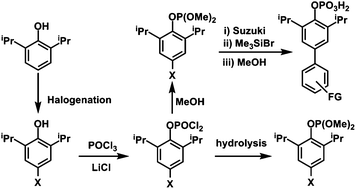
New 4-halo functionalized 2,6-diisopropyl phenyl phosphates, X-dippH2 [(RO)P(O)(OH)2] (R = 4-X-2,6-iPr2C6H3; X = Cl 1, Br 2, I 3) have been synthesized in two steps starting from the corresponding 4-halophenols and characterized by analytical, spectroscopic, and single crystal X-ray diffraction studies. Isomorphous organophosphates 1–3 form a tubular structure in the solid state through extensive hydrogen bonding interactions between adjacent –PO3H2 groups, an aggregation previously unknown among organophosphates and phosphonic acids. The methyl ester of 2, [(RO)P(O)(OMe)2] (R = 4-Br-2,6-iPr2C6H3) (4), was reacted with a series of boronic acids under Suzuki coupling conditions to yield the corresponding C–C bond coupled products, 3,5-diisopropylbiphenyl-4-yl dimethyl phosphate (5), 4′-formyl-3,5-diisopropyl-biphenyl-4-yl dimethyl phosphate (6) and 4′-(diphenylmethyleneamino)-3,3′,5,5′-tetraisopropyl-biphenyl-4-yl dimethyl phosphate (7). The possible reaction conditions for the selective deprotection of phosphate triesters have been established, under which 6 yields 4′-formyl-3,5-diisopropyl-biphenyl-4-yl dihydrogenphosphate (8). Compound 8 is a formyl group functionalized phosphate and shows hydrogen bonding similar to 1–3 forming tubular channels surrounded by peripheral organic groups. The dangling formyl groups in phosphates 6 and 8 undergo intermolecular tail-to-tail hydrogen bonding forming 1-dimensional assemblies in the former and 3-dimensional supramolecules in the latter. Amino and formyl functionalized phosphates may serve as ideal primary building units for building suitably functionalized metal phosphate secondary building units.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...