Amphiphilic cationic copolymers with ciprofloxacin: preparation and antimicrobial activities†
Abstract
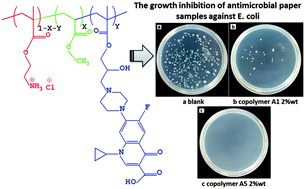
Novel water-soluble amphiphilic copolymers with ciprofloxacin (CPF) and primary amine salt were prepared by the copolymerization of methacrylate monomer containing CPF with protonated primary amine monomer and methyl acrylate (MA). The chemical structure and composition of amphiphilic copolymers were characterized by 1H-NMR, charge density and UV measurements. The antimicrobial activities were evaluated by determining the minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC) against Gram-negative bacterium Escherichia coli (E. coli). The results showed that the hydrophobic MA monomer played an important role in the antibacterial action and the incorporation of ciprofloxacin further enhanced antimicrobial activities of the copolymers. All the copolymers showed excellent antibacterial activities with the MIC values in the range of 5–40 ppm. UV absorption measurements were employed for quantifying the amount of intracellular components leaked into bacterial suspension and revealing the dynamic antimicrobial process of antimicrobial copolymers. The confocal laser scanning microscopy (CLSM) technique was used to assay the viability of bacteria in the presence of antimicrobial copolymers by staining bacteria with specific fluorescent dyes. The results of the shaking flask method of antimicrobial-modified cellulose fibers showed that the copolymers applied to the fibers exhibited excellent antimicrobial activities with complete growth inhibition against E. coli in the presence of 2 wt% (based on oven-dried fibers) of copolymer in the fiber.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...