Effects of preparation conditions on Mn-based activated carbon catalysts for desulfurization
Abstract
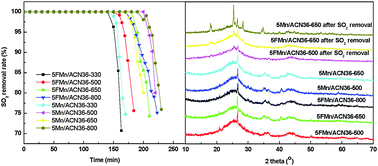
A series of Mn-based activated carbon catalysts were prepared by excessive impregnation with or without ultrasonic assistance, and manganese (Mn) species and surface chemical properties of catalysts before and after SO2 removal were studied. The results showed that different preparation conditions significantly influence the desulfurization activity of Mn-based activated carbon catalysts. The breakthrough sulfur capacity of 5FMn/ACA36 prepared by ultrasonic assisted excessive impregnation is 73.0 mg g−1, while that of 5FMn/ACN36 increases to 126.1 mg g−1. The catalysts exhibit different desulfurization activities when carbon carriers are pretreated with nitric acid at different concentrations, and with the increase of concentrations, the breakthrough sulfur capacity of catalysts increases from 118.1 to 141.6 mg g−1. Catalysts calcined at different temperatures show different desulfurization activities. Both 5FMn/ACW and 5Mn/ACW calcined at 800 °C have the best desulfurization activity, but 5FMn/ACN36 and 5Mn/ACN36 calcined at 650 and 800 °C are similar. The optimal loading of catalysts prepared by excessive impregnation is 7%, but that of catalysts prepared by ultrasonic assisted excessive impregnation is 0.5%. Nitric acid pretreatment can change surface chemical properties and reduce the formation temperature as well as the crystalline size of Mn oxide species such as MnO and Mn3O4. The introduction of ultrasonic oscillation cannot change active species and oxygen-containing functional groups (such as C–O, C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O and O
O and O![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) C–OH) but reduce the active component content to enhance the activity. Mn loading influences the content of active components and oxygen-containing functional groups on carbon supports, leading to a different desulfurization activity. After SO2 removal, MnO, Mn2O3 and Mn3O4 are still observed, but some of them transform into MnO2 with low crystallinity, and some react with generated H2SO4 to form MnSO4, resulting in catalyst deactivation. Types of oxygen-containing functional groups after SO2 removal remain the same but the relative contents decrease, showing that they participate in the reaction of SO2 removal.
C–OH) but reduce the active component content to enhance the activity. Mn loading influences the content of active components and oxygen-containing functional groups on carbon supports, leading to a different desulfurization activity. After SO2 removal, MnO, Mn2O3 and Mn3O4 are still observed, but some of them transform into MnO2 with low crystallinity, and some react with generated H2SO4 to form MnSO4, resulting in catalyst deactivation. Types of oxygen-containing functional groups after SO2 removal remain the same but the relative contents decrease, showing that they participate in the reaction of SO2 removal.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...