Antibacterial activities of polythionates enhanced by carbonates
Abstract
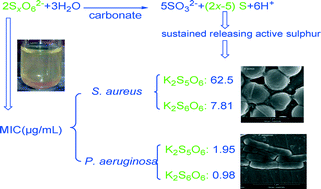
Inorganic antibiotics, with low cost, low occurrence of antibacterial resistance, and long-term effects, have attracted great research interest and have been widely used in many fields. However, few investigations have focused on the antibacterial properties of polythionates due to their synthetic difficulty and commercial unavailability. In this work, the antibacterial properties of polythionates, prepared through a new and facile fabrication method, were measured by minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC), minimum bactericidal concentration (MBC), and cup diffusion methods. Moreover, we have proven for the first time that application of polythionates with different bases (carbonate, urea) exhibits enhanced antibacterial activity compared to application of pure polythionates. The increase in antibacterial activity is related to the formation of active sulfur species from the decomposition of polythionates that is promoted by the increase in pH. The MIC of potassium hexathionate against Gram-positive S. aureus and Gram-negative P. aeruginosa, enhanced by adding potassium carbonate, was 7.81 μg mL−1 and 0.98 μg mL−1, respectively. Therefore, the mixture of polythionate and carbonate is promising as a cheap and sustained antibacterial candidate.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...