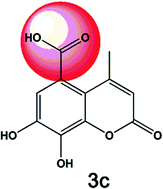
Bladder cancer is one of the most prevalent malignancies of the genitourinary tract, and approximately 25% of patients develop superficial cancers with invasive and metastatic pathology. Coumarins and their derivatives have antiproliferative activity and induce apoptosis in several cancer cell lines. Due to the potential therapeutic applications of these compounds, a series of 4-methylcoumarins were synthesized to investigate the antitumor cytotoxic effect in the T24 and RT4 human bladder cancer cell lines. The microwave-assisted synthesis of the coumarinsvia Pechmann condensation with modifications at position 7 was performed with excellent yields (74–100%). The 7,8-dihydroxy-4-methyl-2-oxo-2H-chromene-5-carboxylic acid derivative (3c) exhibited greater cytotoxicity against T24 cells, which represent a more malignant cell line compared to RT4. In the T24 cells, cell cycle analysis revealed a large number of cells in the sub-G1 phase after treatment with 3c, which is indicative of apoptosis. Apoptotic death was confirmed by annexin V staining assay. Based on the chemical structures of the compounds, it is suggested that the 5-carboxycoumarin ring group has a positive influence on the cytotoxic activity. These results indicate that these new compounds are promising for further chemical modulation to discover a new antitumor agent.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...