Radiosynthesis of high affinity fluorine-18 labeled GnRH peptide analogues: in vitro studies and in vivo assessment of brain uptake in rats†
Abstract
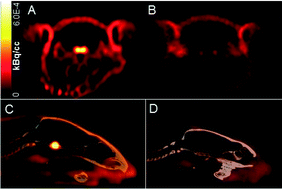
Gonadotropin releasing hormone (GnRH) is recognized as an important neuromodulator affecting behavior and has been associated with the progression of Alzheimer's disease. The peptide has been shown to have a bidirectional transport through the blood–brain-barrier (BBB), which may account for the cognitive effects of systemically administered GnRH. In this study, four novel 18F-GnRH peptide analogues were synthesized and their in vitro and in vivo characteristics studied in male rats. GnRH peptides were assembled by solid-phase peptide synthesis, either as the full length D-Lys6-GnRH (pyroGlu1-His2-Trp3-Ser4-Tyr5-D-Lys6-Leu7-Arg8-Pro9-Gly10-NH2) or as D-Lys6-desGly10-GnRH-NHEt. In all, four GnRH peptide analogues were synthesized and reacted with N-succinimidyl-4-fluorobenzoate (SFB) to yield the fluorinated versions. Binding affinities of the analogues were determined in a competitive binding assay for both human and rat GnRH receptors. Ki-values for the GnRH peptides were found to be subnanomolar, with D-Lys6(FBA)-desGly10-GnRH-NHEt (7) being most potent with a Ki-value of around 50 pM for GnRH receptor species. Radiolabeling was performed using N-succinimidyl-4-[18F]fluorobenzoate ([18F]SFB) in 33.3 ± 12.8% isolated decay corrected (d.c.) yield within 1.5–2 h. Rat serum stability over 2 h revealed minor degradation (≤5%). For in vivo studies, 18F-peptides (4–30 MBq) were injected intravenously via the tail vein into rats and brain uptake was evaluated by means of dynamic PET (2 h) followed by biodistribution studies. PET showed limited or no uptake in brain for the 18F-peptides which predominantly cleared rapidly by renal excretion. Specific binding in the pituitary gland was confirmed for the 18F-peptide, 7, by blocking with the GnRH agonist buserelin.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...