Poly-α,β-aspartyl-Arg-Gly-Asp-Phe: a novel polymeric nanomedicine†
Abstract
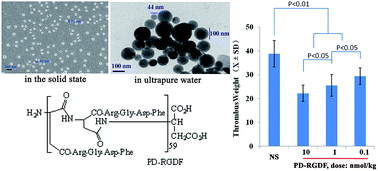
Thrombosis is a pathological condition and has been one of the most prominent causes of morbidity and mortality. Poly-α,β-aspartic acid is a biodegradable polymer, and RGD-tetrapeptides target thrombus. These led to the design of poly-α,β-aspartyl-Arg-Gly-Asp-Phe (PD-RGDF) as a novel polymeric therapeutic drug. In the solid state and ultrapure water PD-RGDF formed nanoparticles of substantially identical diameter. In vitro the nanoparticles inhibited GPIIb/IIIa expression of activated platelets, thereby making the in vitro anti-platelet aggregation efficacy greatly increase. In vivo the anti-thrombotic efficacy of PD-RGDF was 500-fold higher than that of RGDF.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...