Plasma metabolic signatures reveal the regulatory effect of exercise training in db/db mice†
Abstract
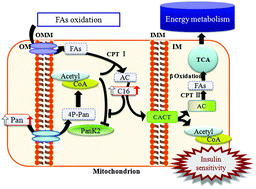
Type 2 diabetes (T2DM) is caused by a complex set of interactions between genetic modifications and life styles. This complexity creates challenges for a full understanding of the altered metabolic pathways that contribute to the development of T2DM, which needs a comprehensive metabolic analysis. Exercise training is a common therapeutic approach known to antagonize the metabolic consequences of T2DM. However, the metabolic phenotypes of exercise effected in T2DM have not been clearly characterized. Here, we present the effect of physical activity on biochemical changes in diabetic db/db mice. An untargeted metabolomics study based on liquid chromatography coupled with high resolution mass spectrometry was carried out to delineate the plasma metabolic signatures in conjunction with a multivariate statistical analysis. As a result, a total of 24 differential metabolites were identified, covering amino acids, organic acids and lipids. Three biomarkers, including lysine, creatine and uridine, were significantly reversed by exercise training in db/db diabetic mice groups compared to lean db/m+ groups. Of note, pantothenic acid and palmitoylcarnitine, which are involved in fatty acid β-oxidation (FAO), were promoted by exercise training in diabetic mice rather than in lean mice. These findings indicated that diabetic mice might be more susceptible to exercise for energy expenditure. Together, the results might demonstrate that exercise could mitigate insulin resistance in T2DM through improving FAO and that uridine in blood might be an important indicator to reflect insulin sensitivity promoted by exercise training in T2DM mice.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...