Insight into the key interactions of bromodomain inhibitors based on molecular docking, interaction fingerprinting, molecular dynamics and binding free energy calculation†
Abstract
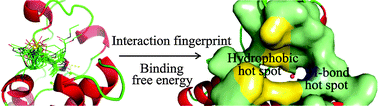
The bromodomain is a key protein–protein interaction module that specifically reads the acetylation marks of histones in epigenetic regulation. Currently, lots of inhibitors targeting the bromodomain have been reported as therapeutic agents. To better understand the interaction mechanism of bromodomain inhibitors, 20 diverse bromodomain inhibitors were studied using a combination of computational methods, including molecular docking, interaction fingerprinting, molecular dynamics simulation and binding free energy calculation. As a result, interactions important for the activity were critically analyzed, and the energy contribution in terms of individual residues was explored. These integrated results provided insights into two hot spots in the active site of the bromodomain, where the hydrophobic hot spot formed by Trp81, Val87, Leu92 and Ile146 played a central role in the interaction, and the hydrogen-bond hot spot mediated by Asn140 exhibited a moderate contribution to the binding affinity of the bromodomain inhibitors. This interaction mechanism study may facilitate the rational design of novel small-molecule bromodomain inhibitors.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...