Shared structural features of the 9aaTAD family in complex with CBP†
Abstract
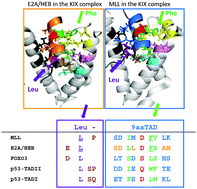
A number of transactivation domains for transcription factors including p53, E2A/HEB, MLL, cMyb, CREB, FOXO3, Gcn4, Oaf1 and Pdr1 have been reported to interact with the KIX domain of general transcriptional mediators CBP, p300 or MED15. Most of those factors belong to the already established Nine amino acid Transactivation Domain (9aaTAD) family. By using available structural data, we found binding analogy for the 9aaTAD in the MLL–KIX and also E2A/HEB–KIX complexes. We recognized two distinct TAD formations in the KIX complex. In the E2A/HEB–KIX complex, the leucine position is determined by the prolonged helical structure including the 9aaTAD and the leucine (long-helical TAD). However in the MLL–KIX complex, the equal position of 9aaTAD and proximal leucine is achieved differently by leucine-turn-helix structural architecture. Furthermore, the FOXO3–KIX complex shares structural analogy with the E2A–KIX complex in respect of both 9aaTAD and proximal leucine. Next, from (i) sequence alignment of the identified 9aaTADs in p53, E2A/HEB and MLL proteins and (ii) the resolved structure of the MLL–KIX and E2A/HEB–KIX complexes, we generated a plausible structural model for p53 that could be used also for other members of the 9aaTAD family. The position of 9aaTADs in Oaf1-, Pdr1- and Gcn4-MED15 KIX complexes and 9aaTAD composition are in good agreement with E2A, MLL, FOXO3 and p53. Analyses of structural data in this study define fundamental structural requirements and shed more light on the ambiguous 9aaTAD domain.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...