A microfluidics approach to study the accumulation of molecules at basal lamina interfaces†
Abstract
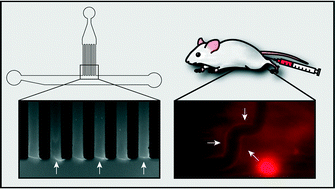
For an efficient distribution of drugs and drug carriers through biological barriers such as the vascular system, the size and surface properties of nanoparticles and molecules play a key role. To screen for important parameters which determine the ability of drugs or drug carriers to translocate through complex biological barriers, an in vitro assay which correctly predicts the behavior of those objects in vivo would be highly desirable. Here, we present a microfluidic setup to probe the diffusive spreading of molecules with different net charges and molecular weights through a basal lamina interface – a biopolymer system which contributes to the barrier function of the vascular system and the skin. From our data, we find a charge dependent accumulation of molecules at the gel interface which is consistent with transient binding of those molecules to the gel constituents. We also observe a similar charge-dependent accumulation of molecules in living mice where the test molecules colocalize with collagen IV, a key component of the basal lamina. Our assay may serve as a platform to perform penetration experiments with even more complex interfaces combining cellular barriers with biopolymer coatings.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...