An automated programmable platform enabling multiplex dynamic stimuli delivery and cellular response monitoring for high-throughput suspension single-cell signaling studies†
Abstract
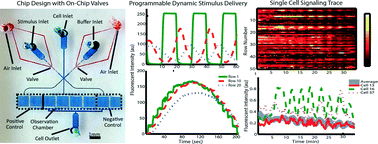
Cell signaling events are orchestrated by dynamic external biochemical cues. By rapidly perturbing cells with dynamic inputs and examining the output from these systems, one could study the structure and dynamic properties of a cellular signaling network. Conventional experimental techniques limit the implementation of these systematic approaches due to the lack of sophistication in manipulating individual cells and the fluid microenvironment around them; existing microfluidic technologies thus far are mainly targeting adherent cells. In this paper we present an automated platform to interrogate suspension cells with dynamic stimuli while simultaneously monitoring cellular responses in a high-throughput manner at single-cell resolution. We demonstrate the use of this platform in an experiment to measure Jurkat T cells in response to distinct dynamic patterns of stimuli; we find cells exhibit highly heterogeneous responses under each stimulation condition. More interestingly, these cells act as low-pass filters, only entrained to the low frequency stimulus signals. We also demonstrate that this platform can be easily programmed to actively generate arbitrary dynamic signals. We envision our platform to be useful in other contexts to study cellular signaling dynamics, which may be difficult using conventional experimental methods.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...