A new high-precision method for determining stable chlorine isotopes in halite and igneous rock samples using UV-femtosecond laser ablation multiple Faraday collector inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry†
Abstract
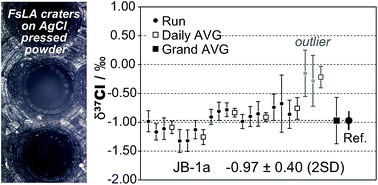
We report a new, rapid method for the high-precision determination of chlorine isotope ratios in halite and AgCl pellets formed from seawater and igneous rock samples. Use of 266 nm ultra violet-femtosecond laser ablation (UV-FsLA) allowed quantitative sampling of halite and AgCl and enabled precise determination of 37Cl/35Cl isotope ratios (δ37Cl) when coupled with a multiple Faraday collector-inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometer (MFC-ICPMS). We used 36Ar+/38Ar+ as an external standard for the mass bias corrections between 39K+–41K+, 36Ar1H+–38Ar1H+–40Ar1H+, and 35Cl+–37Cl+ with isobaric overlap corrections between K+, ArH+, and Cl+ ions. Overlap of the sulfur (36S+) isobar with 36Ar+ was indirectly monitored and corrected by baseline modelling using the 36Ar+/38Ar+ measurement. These procedures collectively helped accomplish an accurate and high-precision measurement of 37Cl+/35Cl+ ratios. Using the proposed analytical method, δ37Cl ratios in natural halite samples were analysed by direct laser ablation. δ37Cl in JB-1a and JB-3 igneous rocks were analysed as AgCl powder pellets produced by pyrohydrolytic separation and co-precipitation of the separated Cl with silver. The external reproducibility of the δ37Cl measurements was ±0.2‰ 2SD (2 standard deviations) for halite and ±0.4‰ 2SD for AgCl precipitate rivalling that of gas source isotope ratio mass spectrometry. The new analytical protocol enabled a precise and rapid δ37Cl analysis of igneous rock samples as AgCl with as little as 4 μg chlorine from the ∼500 μg chlorine separated. This is the first time that high-precision in situ determination of δ37Cl from halite using 4 μg of chlorine has been reported.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...