The role of seaweed bioactives in the control of digestion: implications for obesity treatments†
Abstract
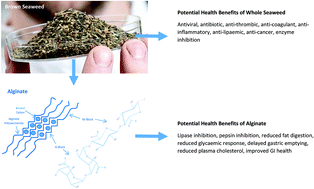
Seaweeds are an underutilised nutritional resource that could not only compliment the current western diet but potentially bring additional health benefits over and above their nutritional value. There are four groups of seaweed algae; green algae (Chlorophyceae), red algae (Rhodophycae), blue-green algae (Cyanophyceae) and brown algae (Phaeophyceae). Seaweeds are rich in bioactive components including polysaccharides and polyphenols. Polysaccharides content, such as fucoidan, laminarin, as well as alginate is generally high in brown seaweeds which are also a source of polyphenols such as phenolic acids, flavonoids, phlorotannin, stilbenes and lignans. These components have been shown to reduce the activity of digestive enzymes, modulating enzymes such as α-amylase, α-glucosidase, pepsin and lipase. This review discusses the effect of several of these components on the digestive processes within the gastrointestinal tract; focusing on the effect of alginate on pancreatic lipase activity and its potential health benefits. Concluding that there is evidence to suggest alginate has the potential to be used as an obesity treatment, however, further in vivo research is required and an effective delivery method for alginate must be designed.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...