Abstract
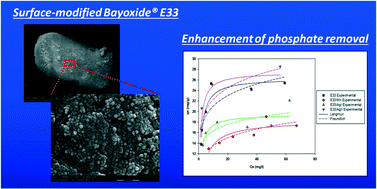
The adsorption of phosphate onto modified Bayoxide® E33 (E33) and underlying mechanisms were comparatively investigated by batch kinetics, sorption isotherms, rapid small-scale column tests, and material characterization. Synthesis of modified E33 was conducted by the addition of manganese and silver nanoparticles on the surface of the goethite (α-FeOOH)-based E33. Upon successful adsorbent synthesis, the materials were characterized using SEM, TEM, XRD, EDX, HR-TEM, and BET surface area analysis. The adsorption kinetics is described by a fast initial adsorption stage followed by a slow adsorption stage, complying with pseudo second-order kinetics and Elovich kinetics. Sorption isotherms revealed that the equilibrium capacity of one of the modified adsorbents (E33/AgII) exceeded that of unmodified E33 likely due to its increased BET surface area. Column experiments confirmed the results for adsorption kinetics and equilibrium of phosphate sorption onto E33 and modified E33. This suggests that media modification has the potential to improve phosphate removal properties.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Celebrating our 2018 prize and award winners

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...